Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that allows computers to learn from data and make decisions without being explicitly programmed.
Instead of following fixed rules, the machine:
- Takes in data
- Learns patterns from that data
- Makes predictions or decisions based on those patterns
How Machine Learning Works
Description: A simple flowchart showing:
Data → Training → Model → Prediction
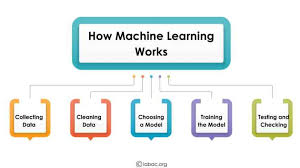
🖼️ Caption:
“Machine Learning teaches computers to learn from data instead of following fixed rules.”
👨🔬 Who Developed Machine Learning?
Machine Learning didn’t come from one person — it evolved over decades:
| Year | Scientist | Contribution |
| 1950s | Alan Turing | Proposed that machines could think and learn. |
| 1959 | Arthur Samuel (IBM) | Coined the term “Machine Learning” and built a checkers-playing program that improved over time. |
| 1997 | Tom M. Mitchell | Gave the first formal definition of machine learning. |
Today, companies like Google, OpenAI, Microsoft, and IBM drive modern ML research.
Timeline of Machine Learning History
Description:
A horizontal timeline with pictures of:
- Alan Turing (1950s)
- Arthur Samuel (1959)
- Tom M. Mitchell (1997)
- Modern AI applications (Google, OpenAI logos)
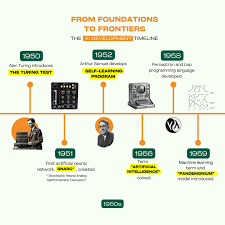
🖼️ Caption:
“From theory to technology — the evolution of Machine Learning.”
🔍 Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning
The model learns from labeled data (data with known answers).
📘 Example: Predicting house prices using data like location, size, and rooms.
- Unsupervised Learning
The model finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data.
📗 Example: Grouping customers with similar buying habits.
- Reinforcement Learning
The model learns by trial and error, improving through feedback.
📕 Example: A robot learning to walk, or AI learning to play chess.
Three Types of Machine Learning
Description:
A three-part graphic:
- Supervised → “Learning from examples”
- Unsupervised → “Finding patterns”
- Reinforcement → “Learning by experience”

🖼️ Caption:
“Different ways machines learn — from examples, patterns, or experience.”
⚙️ How Machine Learning Works
- Collect Data
Example: Images, numbers, text, or customer information - Train the Model
The computer studies the data and learns relationships - Test and Evaluate
Check if predictions are accurate - Deploy and Improve
Use the model in real-world applications and refine it over time
Machine Learning Workflow
Description:
A circular process diagram:
Data → Training → Testing → Deployment → Improvement
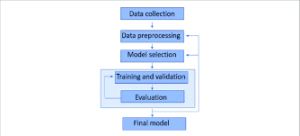
🖼️ Caption:
“Machine learning is a continuous process of learning and improving.”
🌟 Benefits of Machine Learning
| Benefit | Description | Example |
| 🤖 Automation | Reduces human effort in repetitive tasks | Email sorting, chatbots |
| 📊 Better Decisions | Analyzes data for insights | Market forecasting |
| 💡 Predictions | Forecasts future trends | Weather, sales prediction |
| 🔍 Pattern Detection | Spots anomalies and patterns | Fraud detection |
| 🎯 Personalization | Customizes user experience | Netflix or Spotify recommendations |
| ⏱️ Speed & Accuracy | Processes vast data fast | Medical diagnosis, image recognition |
Benefits of Machine Learning
Description:
Icons or illustrations showing automation, prediction, and personalization.
🖼️ Caption:
“Machine learning enhances decision-making, automation, and user experiences.”
🚀 Conclusion
Machine Learning is transforming every industry — from healthcare and finance to education and transportation.
It’s the technology that powers voice assistants, self-driving cars, recommendation systems, and fraud detection tools — making our world smarter and more efficient.